National enrollments decline for sixth straight year, but at slower rate
Enrollment Slide Continues, at Slower Rate
College enrollments in the U.S. decline for a sixth straight year — although at a slower rate — while the bachelor’s degree got more popular.
December 20, 2017
Overall college enrollments in the U.S. have declined for a sixth straight year, according to new data from the National Student Clearinghouse Research Center, but at the slowest pace since the slide began.
The 1 percent decline this fall was due to undergraduate enrollments, which fell by nearly 224,000 students, or 1.4 percent. Graduate and professional programs were up by 24,000 students, according to the center, which tracks 97 percent of students who attend degree-granting institutions that are eligible to receive federal financial aid.
And despite the recent focus by policy makers on associate degrees and certificates, four-year degree programs were the only ones up in the new enrollment data.
Among undergraduates, the center found an enrollment decrease of 2.3 percent for associate-degree seekers, and a 10.7 percent drop for students pursuing certificates or other nondegree credentials. But enrollments were up 1.5 percent among four-year-degree seekers.
Part-time-student enrollments fell by 3.3 percent, according to the report, while the number of full-time students increased by 0.3 percent.
The center also found that enrollments were down for first-time college students. This group saw a 2.3 percent decline, of 63,000 students, compared to the previous fall. Most of the decrease was due to adult students, with the number of first-time students over the age of 24 dropping by more than 13 percent. But 23,000 fewer traditional-age students enrolled in college this fall, a drop of 1 percent. (Adult student enrollments over all have declined by 1.5 million since 2010, the center found.)
“This suggests further declines to come over all in the years ahead, which will continue to present planning challenges for institutions and policy makers seeking to adapt to new economic and demographic realities,” said Doug Shapiro, the center’s executive research director.
Enrollment pressure is a primary driver of the small but growing number of college closures and mergersthat are occurring around the country, experts have said.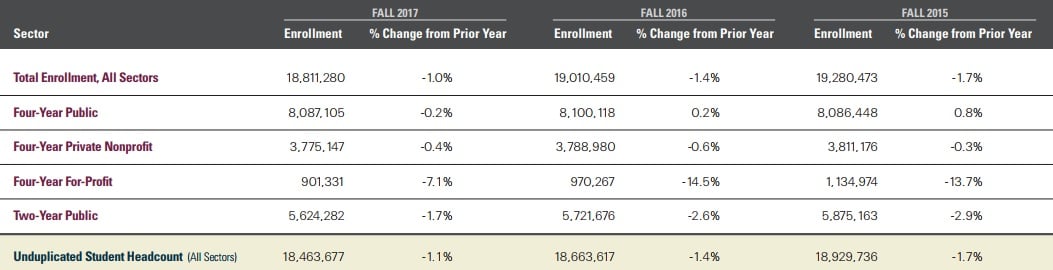
For-profit colleges continue to be battered by sliding enrollments and revenue. The center found that 69,000 fewer students enrolled in four-year for-profit institutions this fall. That drop of 7.1 percent follows several years of even larger declines.
Community colleges have been the second-hardest-hit sector in recent years. But the enrollment decline of 1.7 percent this fall (97,000 students) was less than that of previous years, including the 4.4 percent drop in enrollment at community colleges three years ago.
Enrollments at four-year private nonprofit institutions have been down slightly the last 18 months, a trend that continued with a 0.4 percent decline of 14,000 fewer students this fall.
Four-year public institutions, however, had seen slight enrollment increases in recent years. But that shifted this fall with a small decline of 0.2 percent.
